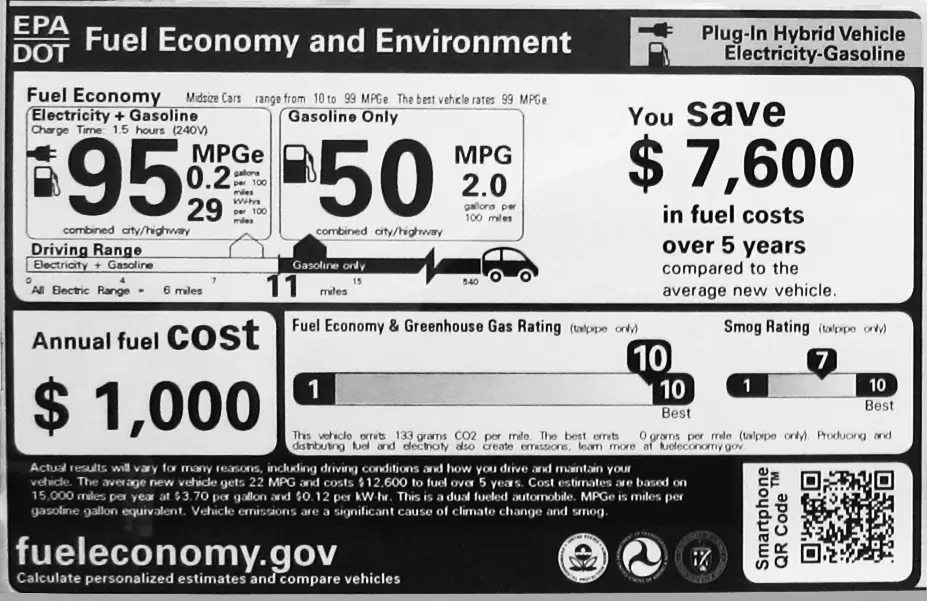
Miles Per Gallon Equivalent (MPGe) is a measure used to compare the energy efficiency of electric and hybrid vehicles with traditional gasoline-powered cars. It shows how far a car can travel using the equivalent energy of one gallon of gasoline.
As electric vehicles (EVs) become more popular, understanding MPGe is essential for consumers who want to compare energy use and fuel savings.
Here are some of the following list of cars from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) data, along with their estimated MPGe:
Electric Cars:
- Tesla Model 3 RWD: 138 city/126 highway/132 combined MPGe
- Lucid Air Pure RWD: 131 city/132 highway/131 combined MPGe
- Hyundai IONIQ 6 SE RWD: 148 city/131 highway/140 combined MPGe
- Tesla Model S: 124 city/115 highway/120 combined MPGe
- BMW i4 eDrive35 Gran Coupe: 109 city/108 highway/109 combined MPGe
Plug-In Hybrids:
- Toyota Prius Prime: 145 city/121 highway/133 combined MPGe
- Lexus NX 450 h+ AWD: 38 city/33 highway/84 combined MPGe
- Ford Escape Plug-in Hybrid FWD: 110 city/100 highway/105 combined MPGe
- Hyundai Tucson Hybrid Blue: 38 city/ 38 highway/38 combined MPGe
- Kia Sportage Plug-in Hybrid AWD: 36 city/35 highway/84 combined MPGe
Hydrogen Fuel Cell Cars:
- Toyota Mirai: 74 city/70 highway/72 combined MPGe
- Hyundai NEXO Blue: 58 city/53 highway/56 combined MPGe
You can see which vehicles offer the most energy-efficient options. The higher the MPGe, the more efficiently the vehicle uses energy.
According to a 2023 report by the U.S. EPA, EVs can save drivers up to 50% on fuel costs compared to gasoline cars.
What Does MPGe Mean?

MPGe lets you see how far an electric car can go using the same energy as one gallon of gas in a regular car.
The EPA created MPGe to help you make intelligent choices when buying a car. By understanding the MPGe meaning, you can easily compare electric, hybrid, and gas-powered cars.
When you are looking for a car, MPGe can tell you:
- How much energy the car uses
- How much it might cost you to run
- How it impacts the environment
For example, a car with a higher MPGe will use less energy to go the same distance as a car with a lower MPGe. It usually means lower fuel costs and less pollution.
EVs are more energy-efficient than gas-powered cars. They convert about 77% of energy into movement, while gas cars only convert about 12-30% of fuel energy.
The EPA also provides a tool called Find and Compare Cars, which allows you to look up and compare the MPGe of different vehicles.
How is MPGe Calculated?
The calculation involves converting electricity use into an equivalent amount of gasoline energy.
Here is how it works:
The EPA determined that 33.7 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity contains about the same energy as 1 gallon of gasoline.
They measure how many kWh an electric vehicle uses to travel 100 miles.
Then they use this formula: MPGe = (100 miles × 33.7 kWh/gallon) ÷ (kWh used to drive 100 miles).
For example, if a car uses 30 kWh to drive 100 miles, it will be MPGe = (100 × 33.7) ÷ 30 = 112.3 MPGe.
For plug-in hybrids, the EPA calculates two values:
- Electric-only MPGe
- Gas-only MPG
They then combine these based on standard assumptions about how much people drive in each mode.
The EPA tests vehicles in a lab using standardized procedures. They run the car on a dynamometer (like a treadmill for cars) through various driving cycles that simulate city and highway conditions. It also ensures that MPGe ratings are consistent and reliable. It sets the testing standards and verifies manufacturers' results. Sometimes, it even tests the vehicle itself to double-check the numbers.
To know more about the EPA's testing procedures, check the “Dynamometer Drive Schedule.”
MPGe vs MPG: What's the Difference?
While they might look similar, they tell you different things about a vehicle's efficiency:
MPG (Miles Per Gallon) is used for gasoline-powered cars. It tells you how many miles a car can drive on one gallon of gas. The higher the MPG, the more efficient the vehicle is with fuel.
MPGe (Miles Per Gallon equivalent) is for electric and plug-in hybrid cars. It tells you how far a car can go using the amount of electricity with the same energy as one gallon of gas.
Let us look at an example:
The 2023 Honda Accord Hybrid, one of the most fuel-efficient gas-powered cars, gets about 48 MPG in combined city/highway driving. Compare that to the 2023 Tesla Model 3 RWD, which gets 132 MPGe in combined driving.
That is almost three times more efficient!
That big difference in efficiency is why the EPA introduced MPGe. They wanted a way to show you just how energy-efficient EVs are compared to traditional cars.
Without MPGe, it would be harder to understand how the electricity consumption of an EV compares to the fuel consumption of a regular car.
MPGe was also introduced to complement MPG because of the:
- Familiar reference point: You are probably used to thinking about car efficiency in terms of miles per gallon, so MPGe uses that same concept.
- Fair comparisons: You can now easily compare the efficiency of all types of vehicles, whether they run on gas, electricity, or a combination.
- Potential savings: When you see how high EVs' MPGe ratings are, you can better understand the potential for lower fuel costs.
- Environmental awareness: Higher MPGe ratings often correlate with lower emissions, helping you make eco-friendly choices.
Factors Impacting MPGe
Your electric vehicle's MPGe can vary based on several factors:
- Vehicle weight: Heavier cars need more energy to move.
- Aerodynamics: Sleeker designs reduce air resistance.
- Driving conditions: Hills, wind, and temperature affect efficiency.
- Driving habits: Rapid acceleration and high speeds use more energy.
- Battery efficiency: Newer batteries often perform better.
- Tire pressure: Properly inflated tires reduce rolling resistance.
- Climate control use: Heating and cooling can drain the battery.
These factors can affect your MPGe, which can differ from the EPA rating. A heavier car or one with poor aerodynamics typically has a lower MPGe.
Driving in extreme weather or hilly areas can also reduce your efficiency.
When choosing an EV, consider how these factors apply to your situation. If you live in a cold area with many hills, your actual MPGe might be lower than the rating.
To get the most out of your EV's MPGe in daily driving:
- Drive smoothly: Avoid sudden acceleration and braking.
- Use eco-mode if available: Use this to optimize your car for efficiency.
- Plan your route: Avoid heavy traffic and steep hills when possible.
- Maintain your car: Keep tires properly inflated and get regular service.
- Pre-condition while plugged in: Heat or cool your car while charging.
- Use regenerative braking: Use recovered energy when you slow down.
- Reduce unnecessary weight: Do not carry items you do not need.
MPGe is just one piece of the puzzle. When choosing an eco-friendly car, consider how and where you will drive, your charging options, the car's range, budget, and local weather conditions.