Emissions from vehicles contain harmful pollutants that significantly contribute to air pollution. This poses a grave threat to the environment and human health. When a motor vehicle emits excessive pollutants, it is an indication that the car requires maintenance to prevent mechanical or engine failure. This is why car emission inspection is a useful tool for keeping a vehicle in good shape.
In addition to ensuring a vehicle’s overall health, car emission inspections are designed to help reduce harmful pollutants emitted by vehicles into the air. These inspections generally check for any harmful pollutants vehicles may release through exhaust fumes while being operated. Car emission inspection is also a legal requirement in many places. It serves as a regulatory mechanism and aims to make vehicles satisfy certain environmental standards and comply with emission standards at a high level throughout their life span.
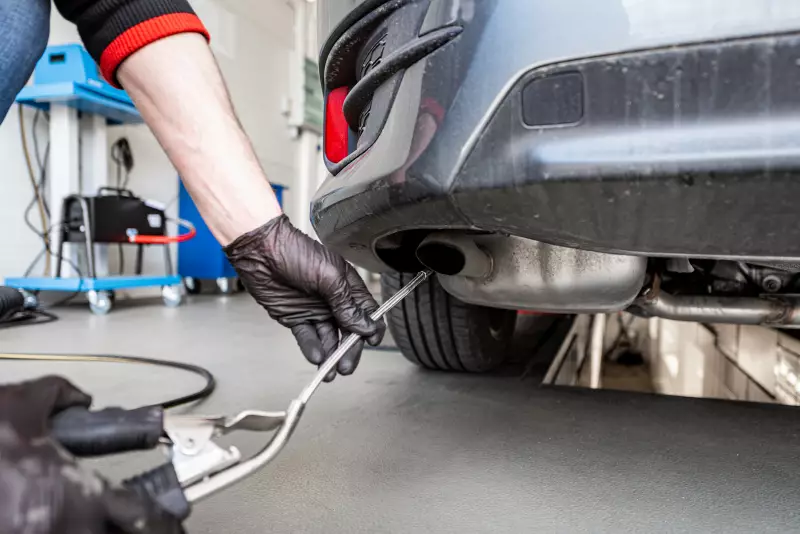

What is an Emissions Test?
An emission test is a type of test conducted to determine the opacity of a car’s exhaust fumes. It helps to ensure that the pollutants and greenhouse gases emitted by a vehicle conform to certain legal limits, depending on location (or state). Emission tests are generally periodic tests required to limit vehicles’ negative impact on air quality and ultimately, the environment. These tests are done to measure exhaust emissions, through which vehicles’ compliance with local emissions regulations and environmental standards may be determined.
The overall purpose of emissions tests is to significantly reduce air pollution, improve air quality, and protect public health. Many studies have revealed that emissions from motor vehicles may cause or worsen certain health issues, such as respiratory diseases and cardiovascular diseases. Each time vehicle owners hit the gas pedals or rev their engines, combustion takes place, which typically releases some harmful gases into the air. Emissions testing generally helps in curbing such greenhouse gas emissions. Therefore, its critical role in combating global climate change and ensuring a healthy environment cannot be overstated.
What States Require Emissions Testing?
Some states in the United States require emissions testing or a form of smog checks. However, testing requirements may vary by state, and specific regulations may vary within each state. While some states mandate emissions testing statewide, others only do partial smog checks in specific jurisdictions. The table below shows what states require smog checks and the regional variations among them:
|
State |
Emission Inspection Requirements/Regional Variation |
|
Arizona |
Inspection is needed in the Tucson and Phoenix metropolitan areas. The inspection must be done before vehicle registration. |
|
California |
Inspection is required statewide, but requirements generally vary by location. Certain vehicles are exempt from smog checks. |
|
Colorado |
Biennial emission inspection is required in specific counties, including Boulder, Jefferson, Arapahoe, Adams, Larimer, El Paso, Douglas, Weld, Denver, and Pitkin counties. Vehicles less than 8 years old require smog checks every other year. |
|
Connecticut |
All vehicles registered in the state need biennial emissions testing. |
|
Delaware |
Smog checks are required for all vehicles manufactured since 1968. However, motor vehicles manufactured within the last seven model years are usually exempt from emissions testing. |
|
District of Columbia (Washington, D.C.) |
Registered vehicles require biennial smog checks, but zero-emission vehicles, new motor vehicles with a certificate of origin, and pre-1968 vehicles are generally exempt from emissions testing. |
|
Georgia |
Annual emissions testing is required in certain counties, including Fayette, Cobb, Cherokee, Henry, Rockdale, Douglas, Coweta, Clayton, DeKalb, Gwinnett, Paulding, Forsyth, and Fulton counties. |
|
Illinois |
Annual emissions testing is required for eligible vehicles in the East St. Louis and Chicago metropolitan areas. |
|
Louisiana |
Annual emissions testing is required. Counties such as East Baton Rouge, Livingston, Iberville, Ascension, and West Baton Rouge have enhanced inspection and maintenance programs that help control car emissions. |
|
Maine |
Smog checks are required for most original vehicle registrations, while annual emissions testing is required for motor vehicles registered in Cumberland County during registration renewals. |
|
Maryland |
Biennial emissions testing is required for most vehicles in the Baltimore-Washington metro area. |
|
Massachusetts |
Annual emissions testing is required. |
|
Missouri |
Biennial emissions testing is required in Franklin, St. Louis, Jefferson, the City of St. Louis, and St. Charles counties. However, new vehicles, older gasoline vehicles, and diesel-powered motor vehicles may be exempted. |
|
Nevada |
Emissions testing is not mandatory. However, it is required annually for motor vehicles from model years 1968 and newer in the urban areas of Washoe and Clark Counties or the Reno and Las Vegas areas. |
|
New Hampshire |
Annual emissions testing is required for passenger vehicles less than 20 years old. |
|
New Jersey |
While most vehicles need emissions testing, certain classes of motor vehicles only require biennial smog checks. |
|
New Mexico |
Vehicles model years 1990 and newer weighing up to 10,000 lbs in Bernalillo County require biennial emissions testing. |
|
New York |
Annual emissions inspection is required for all vehicles. |
|
North Carolina |
Vehicles in over 20 out of 100 counties require annual emissions testing. These counties are Cumberland, Alamance, Catawba, Randolph, Wayne, Wake, Forsyth, Gaston, Franklin, Guilford, Iredell, Rowan, and Orange. Others include Union, Stanly, Chatham, Buncombe, Davidson, Lee, New Hanover, Mecklenburg, Durham, and Johnston. |
|
Ohio |
Smog checks are required in seven Northeast counties in the Cleveland metro area. They include Geauga, Summit, Lake, Cuyahoga, Medina, Portage, and Lorain counties. However, motor vehicles 4 years old and newer, as well as those older than 25. |
|
Oregon |
Depending on the age, vehicles in the Medford and Portland metro areas require periodic emissions testing. |
|
Pennsylvania |
Periodic emissions testing is required in over 20 counties located in the Pittsburgh and Philadelphia regions, as well as the Central Pennsylvania area of the state. Generally, vehicle owners must undergo smog checks before registering their vehicles in these counties. |
|
Rhode Island |
Biennial emissions testing is required for most vehicles in the state. |
|
Texas |
About 17 out of the state’s 254 counties require emissions testing. |
|
Utah |
Biennial smog checks are required for most vehicles with model years less than 6 years old in populated counties like Salt Lake, Cache, Utah, Weber, and Davis counties. |
|
Vermont |
Most vehicles 16 years old or newer require annual emissions testing. |
|
Virginia |
Biennial emissions testing is needed for most vehicles 1,000 lbs or less in the Northern region of the state. |
|
Wisconsin |
Biennial emissions testing is needed in some of the southeastern |
What Do They Check for During an Emissions Test?
Generally, vehicle emissions testing checks for basic emissions within the exhaust and evaporative emissions. The exhaust gas analysis is done to test for varying pollutants. In addition, during smog checks, a vehicle’s ECM (engine control module) is tested to ascertain it satisfies going standards for its make and model.
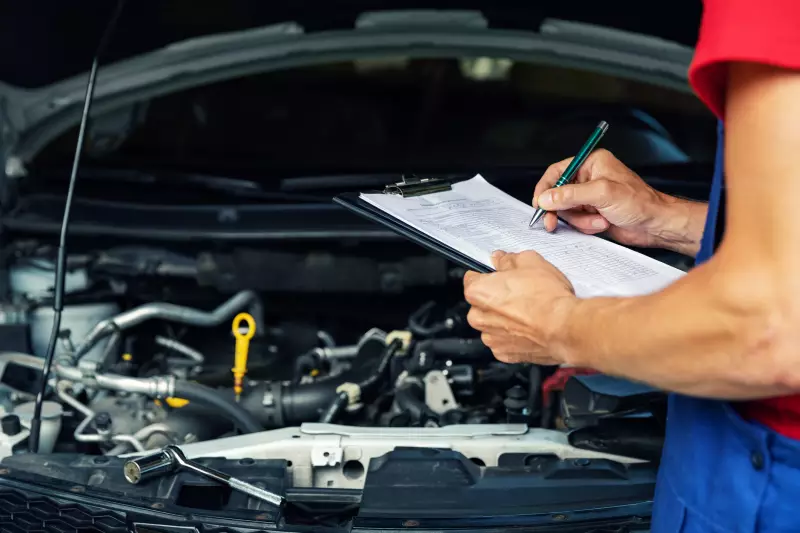

Exhaust Emissions Testing
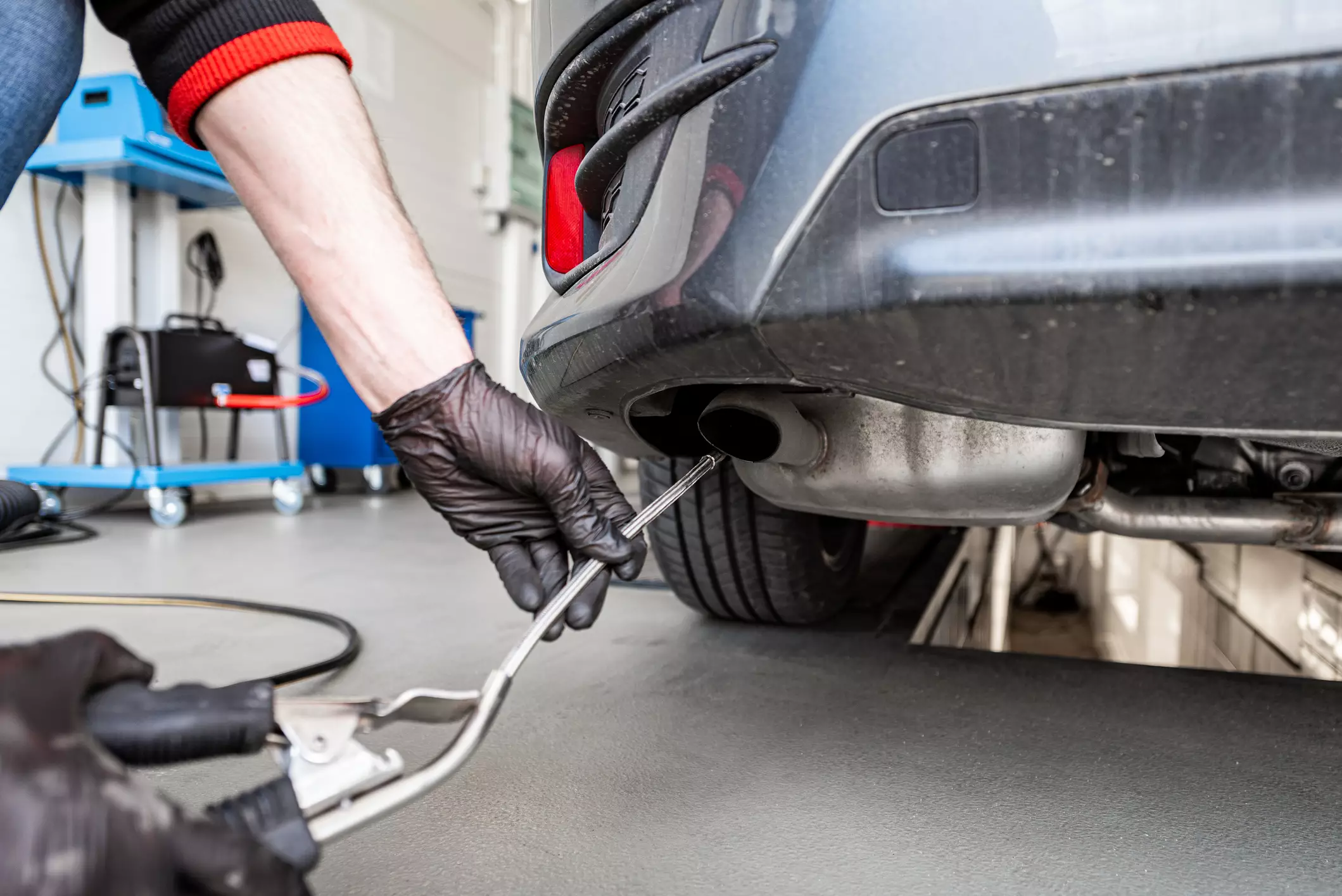
Exhaust emissions testing is generally conducted for older model year vehicles, as they rarely have onboard computers. It is conducted by hooking up an exhaust gas analyzer to a car’s tailpipe to collect samples of emissions, which are then analyzed. Typically, exhaust emission testing checks for the amount of hydrocarbon (HC), carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO2), and Oxygen (O2) emitted by a vehicle. In addition to these, other tests may measure the amount of nitrogen oxide (NO). If the vehicle runs on a diesel engine, a diesel exhaust analyzer is what is often used, and, in addition to measuring gas emissions, it will check the amount of soot.
On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) System Check
A vehicle’s on-board diagnostics (OBD) system is designed to monitor the performance of major engine components, which includes detecting and reporting abnormalities in emissions output. During emissions testing, the technician will inspect the check engine warning light and other indicators to determine if the vehicle is properly controlling harmful gases. Several of these indicators may need to be reset if a car’s battery was recently disconnected. Otherwise, the vehicle may fail the smog checks. A vehicle may have to be driven at various speeds for a couple of days to reset the indicators.
Catalytic Converter Evaluation
Motor vehicles powered by an internal combustion engine have catalytic converters in their exhaust systems to serve the purpose of emissions control. A catalytic converter evaluation in an emissions testing generally assesses the function and condition of a vehicle’s catalytic converter to determine if it can properly convert harmful exhaust gases into less harmful gases. It is done by comparing the level of pollutants released by a vehicle before the converter to the level of such pollutants after using a converter.
Fuel System and Engine Performance
Beyond checking the amount of greenhouse gases released, emissions testing generally evaluates a vehicle’s overall engine efficiency and fuel system performance. Generally, the state of a car’s engine and fuel systems directly impacts the level of pollutants emitted, and any issue with either system may indirectly cause higher emissions of pollutants.
For instance, emissions testing will check for an issue with the fuel injector or pump that may cause poor combustion, leading to increased emissions. Similarly, a smog check will assess engine performance by evaluating the health of the oxygen sensor or EGR valve. There could be increased emissions of CO and HC if these components malfunction.
Additional Emission Systems Checked
Other vehicle emission systems checked by a typical emission testing include the following:
- Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Valve - A check for this system evaluates a vehicle for proper valve operation and flow.
- Evaporative Emissions System - During emissions testing, filler tank, fuel tank, and other key components of this system are visually inspected to ascertain that no fuel vapors are escaping into the air.
- Acceleration System - Acceleration simulation mode test comes in handy in analysing exhaust gas, where the analysis cannot be done while a vehicle is idling. To perform this test, a car is placed on a treadmill-type device and subjected to the motions of driving and acceleration.
Consequences of Failing an Emissions Test
When a vehicle fails an emission test, it means it exceeds the allowable air pollution limits. This is basically a prompt to a car owner to address environmental concerns and ensure a motor vehicle satisfies regulatory standards. In many cases, the report of emissions testing will list the details of pollutants that exceed the acceptable standards and recommend the repairs that need to be done.
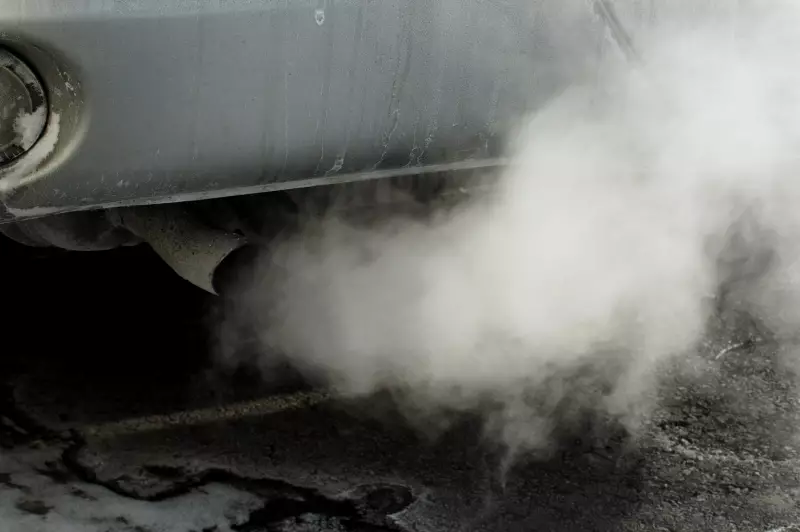

It is important to repair all the components diagnosed as needing fixing in the report so the vehicle can comply with regulatory standards. Re-testing is usually legally mandated. Emissions-related repairs may include air injection, fuel delivery, catalytic converter, air induction, evaporative emissions, EGR, oil and filter change, internal engine parts, and electronic engine controls. After repairs, a retest will have to be done to verify compliance.
Furthermore, if a vehicle owner fails to address the emissions problems identified after smog checks, they may be subjected to certain penalties. Such penalties may include car registration suspension and/or fines. Also, when a vehicle fails emissions testing, the relevant regulatory agencies may typically impose restrictions on the use of such a motor vehicle. The imposed limitation is paramount to reducing the environmental impact of the high-emitting vehicle