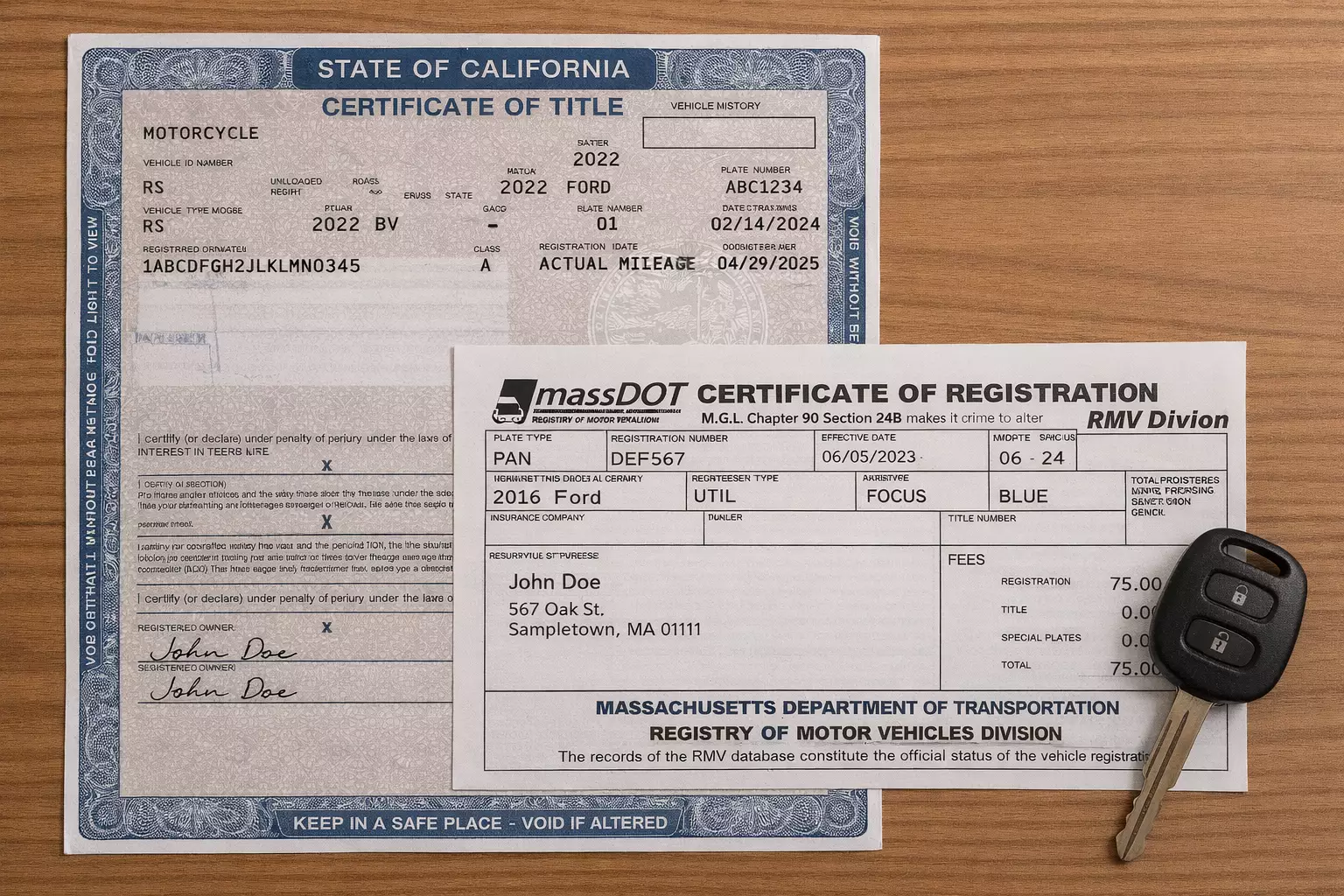
Many drivers confuse car titles and registrations, but they are not the same. Each document serves a distinct legal purpose. A vehicle title legally proves who owns the car, while a car registration shows the vehicle has legal permission to be driven on public roads.
When selling, buying, or transferring ownership of a vehicle, it is important to understand the difference between a car title and registration. You also need to know why both documents matter, when each is needed, and how to verify a vehicle’s title history with tools like the GoodCar Vehicle VIN Check.
What Is a Car Title?
A car title is the legal proof of a vehicle’s ownership and is typically issued by your state’s Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV) or a similar agency. Because the document shows who officially owns a motor vehicle, it is required when a vehicle’s ownership is about to change from one person to another. For example, it is needed during a car sale, when paying off a car loan, or during the title transfer process.
While the specific information included in a vehicle title can vary slightly by state, a typical title contains important details about the owner, the car, and any outstanding financial interests. These details include the owner’s full name and address, the car’s make, model, and body type, and the vehicle identification number (VIN). Other information includes the odometer reading at the time of issuance, technical information, and lienholder information if the vehicle is financed.
A car title establishes legal ownership, and without it, nobody can sell, transfer, or register it in another person’s name. Before buying a used vehicle, check the car’s title history and ownership records using tools like GoodCar’s VIN Check. The report will reveal information such as title brands, past owners, and accident history, which can help you avoid problems like liens, rebuilt titles, and salvage titles. These titles often complicate ownership transfer and may reduce vehicles’ resale values.
What Is Vehicle Registration?
Vehicle registration is proof that a car has been properly documented with your state’s Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV) and is legally permitted to be driven on public roads. The DMV or other relevant licensing authority issues you a registration card, a license plate, and sometimes a registration sticker, depending on the state. A registration sticker is either displayed on your windshield or license plate.
Information contained in vehicle registration can vary by state. However, it typically has details about the vehicle and the registered owner. These details include the registered owner’s name and address, license plate number, the car’s VIN, specifications (make, model, and year), proof of insurance coverage, and the registration expiration date.
You must renew your vehicle registration periodically to avoid associated fines and penalties. This can be annually or biannually, depending on the state. Check your state DMV office for renewal rules. Each state also has its unique renewal requirements, but they typically include payment of registration fees and proof that the vehicle meets local emission and insurance requirements.
When selling or purchasing a car, updating the registration is separate from the title transfer process. The new owner of a vehicle must complete a fresh registration to be able to legally drive it on public roads, even if the title changes hands. If you are buying a used car and are unsure about its registration status or history, use tools like GoodCar’s VIN Check to confirm whether the vehicle has a valid registration.
Key Differences Between Car Title and Registration
Car title and vehicle registration are two different documents with unique legal functions, even though many drivers use both interchangeably. It is important to know the distinctions between these terms to avoid confusion during a title transfer, when buying a used car, or during car registration renewal.
The table below highlights the major ways a car title is different from vehicle registration:
| View Point | Vehicle Title | Car Registration |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Primarily serves as proof of ownership of a car | Serves as proof that a vehicle has been legally registered with the relevant agency and authorized to be driven on public roads |
| Content |
Owner’s name, address, car make, model, year, vehicle identification number VIN, body style, color, issuance date, title brands, and lienholder information (if applicable) |
Owner’s name, address, VIN, license plate number, insurance coverage details, expiration date, odometer reading at the time of registration, and vehicle weight |
| Issuing Agency | State Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV) or any other authorized state agency, depending on the state | Authorized state vehicle licensing authority or the Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV) |
| Uses | Selling or buying a car, verifying lien release, transferring vehicle ownership, or checking a car’s title history | Required to drive legally on public roads, confirm insurance compliance, and pay state-specific fees |
| Need for Renewal | Renewal is not required. It is only issued once. However, you may need to get a new one if you make significant changes to the vehicle, a lien is added or released, or ownership changes | Annual or biannual renewal required, depending on state law |
| Verification Method | VIN Lookup | DMV record check or license plate lookup |
| Legal Importance | Helps confirm the owner of the vehicle | Confirms the car is roadworthy |
| Associated Fees | One-time title fee unless title transfer is required or replacement is needed | Varies by state, but there are usually ongoing registration fees and taxes |
| Document Custody | The car owner or lienholder if the vehicle is financed | The registered car driver |
Both the car title and vehicle registration are essential for legal ownership as well as operation. While registration confirms that a vehicle satisfies state requirements to be driven legally, a car title generally proves ownership. When shopping for a used car, be sure to check both the registration and title history using tools.
Common Situations Where Confusion Happens
Drivers sometimes confuse car titles with vehicle registration documents, and the reason is not far-fetched. Both documents are typically issued by the Department of Motor Vehicles or an equivalent agency and often contain similar information. However, since they serve distinct legal purposes, you must be careful not to mix them up to avoid costly mistakes or delays in ownership transfers, especially when selling or buying a used car.
Here are common real-life situations where drivers often confuse a car registration with vehicle registration (or vice versa) and how to handle each one:
- Buying or Selling a Vehicle - When you sell or buy a vehicle, there must be a car title transfer process between the seller and buyer to establish new legal ownership. Subsequently, the new owner must update or renew the vehicle registration in their name before they can legally drive it. Remember to verify a vehicle’s title history before buying it.
- Paying Off a Car Loan - If your car was financed, the lienholder, a lender or bank, keeps the vehicle title until you pay the loan in full. Once you finish making payments, the lienholder issues a lien release, after which the vehicle title is updated to reflect your name as the full legal owner. If you are in this situation, be sure to request an updated clean title after the lien release.
- Relocating to Another State - If you move to another state, you may need to transfer the title to the new state’s DMV system, depending on state law. In most cases, you must register your vehicle in your new state once you move across state lines, which requires obtaining a new license plate and registration card. To avoid delays caused by mismatched ownership data or outdated lienholder records, make sure to confirm your current title status before applying for new registration in your new state.
- Leasing a Vehicle - If you lease a car whose title is held by the leasing company, the company remains the legal owner listed on the title, but you are responsible for registration and insurance. However, if you opt to buy the car after the lease ends, the title must be transferred to your name. Until you buy the vehicle, do not confuse the ownership of the vehicle (car title) with the registration in your name.
- Lost or Damaged Documents - Are you confused about what to do after losing your vehicle registration or car title or if they are damaged? For car registration, request a registration replacement quickly from the DMV or authorized licensing authority. You can do this online in most cases. For a lost or damaged vehicle title, request a duplicate title from your state’s DMV. Be sure to keep digital copies of both documents, as you may need them as proof of ownership if they are damaged or lost and you are requesting a replacement.
It is easy to avoid the common mistakes drivers make regarding car titles and vehicle registration. Just understand that the registration shows the car is legally permitted on the road, while the title proves the real owner of the car. Whether buying or selling a new car, moving between states, or paying off a loan, confirm the vehicle’s title status, lien history, or registration validity using tools like GoodCar’s Vehicle VIN Check.
How to Check Car Title and Registration History
Many buyers assume that a valid car registration means everything is fine, but that is not always the case. Before paying for a used car, be sure to check the title and registration history to know if it is properly registered, legally owned by the seller, and free from hidden issues. Sometimes, a car with a clean registration may have a salvage or branded title, making it difficult to insure and lowering the vehicle’s resale value. Checking a vehicle title and registration history can help you avoid scams and protect yourself from future ownership disputes.
Below are a few steps to check a car title and registration history, especially if you are shopping for a used vehicle:
- Conduct a VIN Lookup to Check Car Title History - You can uncover important details about a vehicle by running a VIN title check using tools like GoodCar’s Vehicle VIN Check. Such details typically include the following:
- Current title status, which can be clean, rebuilt, salvage, lemon, or junk
- Previous ownership history
- Title history reports, including ownership changes, lien releases, and accident records
- Odometer readings and any mileage discrepancies
- Lienholder information indicating whether the vehicle is financed or paid off
- Title transfer records for transfers across different states
- Check Car Registration Status - After obtaining various reports on a vehicle’s title history, confirm that the car registration is valid and current by contacting your state DMV. Most states DMVs offer online vehicle registration lookup services through their websites. Alternatively, you can perform a license plate lookup on GoodCar’s License Plate Lookup to check a car’s registration status. If you are buying a vehicle from another state, ensure that the registration details match the title information.
- Double-Check Registration and Title for Accuracy - Next, compare the information obtained from the DMV registration record and VIN title check for any discrepancies. Mismatched or inconsistent data across both documents may indicate improper transfers, title fraud, or outstanding liens.

FAQs About Car Titles and Registrations
Below are answers to some of the most frequently asked questions about car titles and vehicle registrations to help you understand how each works:
Do I Need Both a Title and Registration to Drive Legally?
Yes. Both a vehicle registration and a title are required to drive legally. You cannot legally drive on public roads without a car registration, even if you hold the title. The title is legal proof that you own the vehicle; you also need it to operate your vehicle legally.
Can I Register a Car Without a Title?
You typically need a valid car title to register a vehicle because it serves as proof of ownership. However, some states may allow you to obtain a temporary or bonded registration if there are title issues that must be resolved before proper registration can be issued.
Who Holds the Car Title if I Have a Loan?
Until you pay your car loan in full, the lienholder (lender or bank) usually holds the vehicle title. You will receive a clean title in your name once you make the final payment.
What Happens if My Registration Expires?
You must renew your car registration once it expires, as driving with an expired registration is illegal and subject to fines and penalties. Depending on your state’s laws, renewal may be required annually or biannually.
Is the Title the Same as Proof of Insurance?
No. A car title is a separate document from proof of insurance. While a vehicle title shows ownership, proof of insurance confirms that the vehicle is covered under an insurance policy. You need both documents, along with a valid registration, to drive your car legally.
How Do I Replace a Lost Car Title or Registration?
To replace a lost vehicle registration, submit a request for registration card replacement online or in person at your state Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV) office. For a car title, submit an application, identification, and the applicable fee to the DMV to request a duplicate.