What Is A Car Title: Definition & Different Types
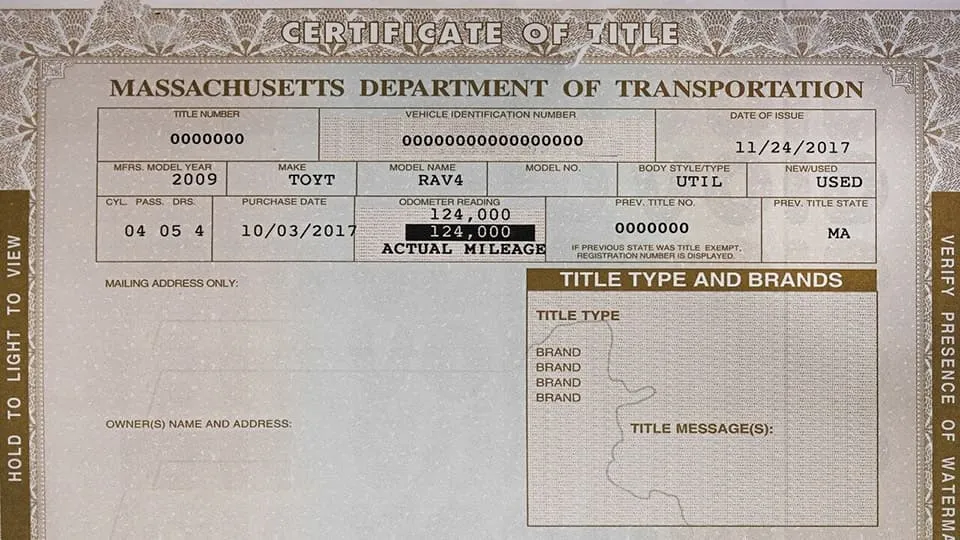
When you purchase a car, you will receive an important document known as a car title. This document legally proves that you are the current owner of the vehicle and are required to register your car with the local Department of Motor Vehicles.
No matter the nature of the purchase, whether from a new or used car dealership or even a private citizen, the seller is legally obligated to provide you with a valid car title. There are several key pieces of information on the document and various types of vehicle titles you may receive.
What Is a Vehicle Title?
A vehicle title is the document you receive when purchasing a vehicle that shows any governing body or law enforcement agent you are the car's legal owner. Besides your vehicle title number, your car title will include important details like:
- Name and Address: Your title will have your full legal name and current address printed on it to help identify you as the legal owner.
- License Plate Number: Your full license plate number should be printed on your car title near your name and address.
- VIN Number: Your vehicle identification number, also known as a VIN, is a 17 character sequence of numbers and letters. This number will be unique to your vehicle and is one of the best tools to help identify you as the car's owner.
- Make, Model and Year: A car title will also contain the vehicles make, model, and year; a vehicle's make refers to the manufacturer who created the car, the model is the name of the line of products that vehicle is in, and the year is simply the year the car was constructed.
- Technical Information: The technical information section of your car title will have details relating to the vehicle's power, purchase price, and gross weight. It also may have additional technical details depending on the vehicle's manufacturer and total age.
- Lienholder Information: A lien is a lender's way of assuring they will receive repayment for a loan. As the lienholder, the lender will need full payment before a car can be resold. Your auto title should contain all information related to liens and the lienholder.
What Are The Different Types Of Car Titles?
While there are more than 65 types of car car titles, these ten are the most common:
- Clean
- Junk
- Salvage
- Reconstructed
- Bonded
- Rebuilt
- Affidavit
- Odometer Rollback
- Water Damage
- Dismantled
Clean
The best possible option you can have is a clean car title. These titles make it easy to get a car loan and indicate that the car has never been deemed a total loss by insurance or salvaged. In addition, vehicles with a clean title generally command a higher resale value.
Junk
A car with a junk title is destined for the scrapheap; this title of car indicates that the vehicle has been sold to a junkyard and will likely be disassembled and sold for parts and scrap. In some jurisdictions, junk and salvage titles are one and the same.

Salvage
If a vehicle decreases in value by a significant amount (generally more than 75% of what it was worth originally) due to an accident or damage, it's given a salvage title. Usually salvage vehicles may not be driven legally on the roads. They can be used for parts however.
Reconstructed
When a vehicle is modified or repaired significantly, it's given a reconstructed title. This title can be issued by the body shop, collision center, vehicle rebuilder who completed work on the car, or an insurance company. Much like a salvage vehicle, a reconstructed car can be legally driven as long as the vehicle passes a road safety inspection.
Rebuilt
Similar to reconstructed, a rebuilt title means that the car has been revamped to a certain degree. This document can be issued by the place where the vehicle was rebuilt or by an insurance company. As with a reconstructed car, a rebuilt car is legal to drive if it passes an inspection for road safety.
Bonded
If your vehicle is missing certain ownership documents like the original title, you will be given a bonded title. Also known as a certificate of title surety bond, this document establishes you as the owner of the car despite lacking a way to legally prove you had the original title. To get this vehicle title, you have to purchase a surety bond.
Odometer Rollback
An odometer rollback title, also known as a TMU brand, is given when a vehicle has probably been tampered with via odometer rollback. Odometer rollback is an action scammers will take to artificially reduce the vehicle's mileage. Due to this, it's impossible to tell the true value of the vehicle, and the DMV will give it a TMU title to indicate this fact. Cars with this title are next to impossible to insure and often far harder to sell.

Water Damage
If a vehicle gets damaged from flooding, hurricanes, or an accident resulting in the car being submerged, it will likely get a water damage title. Also known as a flood title, once a vehicle sustains a certain level of water damage (usually enough to fill the engine compartment), it will receive this designation. Therefore, cars with water titles need to be carefully inspected before purchase, as they could be severely damaged.
Dismantled
In the same family as the junk and salvage titles, a dismantled title is given to cars that have been heavily damaged. Usually, if the total cost of parts would be more than the current car value, the owner will get a dismantled title'; this allows them to sell the remaining functioning car parts.
Car Title Frequently Asked Questions
What Is A Car Title?
A car title is a legal form establishing that you or a business are the legal owner of a vehicle. They are issued by the state the car was purchased in, usually by the Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV) or Department of Licensing (DOL).
How Much Does A Car Title Cost?
The only fees associated with a car title are incurred when that title is transferred. If you, or a dealership, sell a vehicle, they need to pay a fee and transfer the vehicle within a certain amount of time after filing. These fees can range from $15 to $150, and fines can be incurred if the transfers are not completed within the allotted time. For example, Washington gives sellers ten days to transfer the vehicle before they incur a $50 failure to transfer fine.
What Does A Car Title Look Like ?
Often referred to as a pink slip, the car title no longer has the pink color they were once associated with. Your vehicle title will likely be in a light blue or green, and include the name of your state at the top. It will then say "certificate of title for a vehicle, and have all the relevant information relating to the vehicle below.
How To Get A Title For A Car?
You as the buyer and the seller (likely a dealership) must both submit paperwork to the DMV or DOL within five days of the sale's finalization. The dealership will sign a title over to you, and after submission, the DMV or DOL will issue your new car title in the mail.
How To Transfer A Car Title To A Family Member?
In a similar process to the initial sale, transferring ownership of a vehicle to a family member involves similar documentation, signing, and submission of associated materials. The family member in question must apply at the DMV, pay the fee, and wait for the auto title to be mailed.
How To Get A New Title For A Car?
Getting a new title involves finding the proper forms on your local DMV website, completing and possibly notarizing the forms, then turning them in. You'll likely have to wait several weeks to get the new title in the mail.
What Is The Difference Between Title and Registration?
While a car title establishes you as the legal owner of your new vehicle, a car registration shows you've paid all necessary fees with the state, passed a vehicle safety and emissions inspection, and the car has been deemed legal to drive.
When you purchase a new or used car, the dealership may provide you with a temporary registration. These documents are usually valid for up to 30 days, and you'll get a paper tag to display in your vehicle. A car's registration has to be renewed every couple of years, while a title only changes when the owner of the vehicle changes.
How Should I Store My Car Title?
Treat your auto title like you would social security cards, passports, and birth certificates. Take extra care when storing this document, and if possible, don't keep it in your car like you would with a registration. If your state has the option, try to get a digital copy of your vehicle title. This way you don't have to worry about the physical document being damaged or lost. You can find information on electronic car titles through your local DMV branch.
What Happens If You Lose Your Car Title?
While the procedures to replace a lost title vary from state to state, the first step is to visit your state's Department of Licensing (DOL) or Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV). They will guide you through the process of title replacement. This process usually involves:
- Filling out an Affidavit of loss/release of interest form.
- Having the registered owner (most likely you) sign the form and getting the form notarized.
- Mail the completed form or bring it in personally to a DOL or DMV office.
You will likely have to pay a replacement fee to receive your new document and then wait a set period of time. But, again, both the fee and waiting period vary depending on the state your vehicle is registered in. In Washington, for example, the vehicle title replacement fee is $35.50, and the replacement title will take 8 to 10 weeks to reach you.
Where Can I Find More Information About My New Vehicle?
Your car title will contain valuable information about your new vehicle, but it doesn't have everything. If you want to find a complete vehicle history report, comprehensive recall list, or complete a VIN lookup, you'll need to use a vehicle history search tool. At GoodCar, we collect vast amounts of data for verifiable and relevant information about your vehicle. You should have the same information a dealership has when dealing with a new or used vehicle, and we want to help. Try our service today!
FREE Vehicle Search
- Accidents
- Problem Checks
- Title Records
- Recalls
- Values
- Specs
-
InfoPay, Inc. (dba GoodCar) is an Approved NMVTIS Data Provider
-
-






























