The diesel particulate filter (DPF) was introduced in the mid to late 2000s in some diesel engines, and its primary purpose is to trap diesel particulate matter yet to be burned in the engine. Diesel particulate matter is a classy name used to describe exhaust soot, the black soot typically associated with diesel. Before the mid-2000s, when the DPF was introduced, the thick, dirty black smoke/soot from rail trains and old buses was common. However, this is fast becoming a thing of the past. The DPF was designed as one of the most effective technologies for emission control systems in diesel engines, capturing the black soot produced by such engines.
What Is a Diesel Particulate Filter?
A diesel particulate filter (DPF) is a special filter found in various types of car engines, especially in modern diesel engines. It captures and stores diesel particulate (exhaust soot) emitted from diesel engines and prevents their emissions from entering the atmosphere. Typically, diesel particulates harm the environment and pose serious dangers to human health. The primary function of a DPF is to minimize the number of harmful exhaust soot that escapes the exhaust systems of diesel engines and make the air surrounding us cleaner and safer to inhale. While the DPF captures particulate matter, it is not meant to store it permanently. Instead, it is designed to trap larger exhaust soot particles that have not been burned in the engine so they can be completely burned into smaller sizes. After complete combustion, they can then pass through the filter and escape the exhaust pipe.
The DPF is now mandatory for vehicles with diesel engines to comply with certain exhaust emissions regulations or standards. For example, it is required to meet the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulations on all air pollution caused by diesel exhaust, including carbon emissions. It is considered unlawful under the Clean Air Act, Section 203, for anyone to remove, alter, or be involved in knowingly or unknowingly deleting the DPF system of a truck. The DPF system is the entire system of parts, including the filter itself.
How Does a Diesel Particulate Filter Work?
Most diesel particulate filters (DPF) are made from ceramic materials because they provide excellent stability and thermal resistance. The most commonly used ones are the cellular ceramic honeycomb filters with channels blocked at each end. The blocked ends typically force the exhaust gas containing particulate matter through the DPF wall. While the DPF traps the harmful soot particles within its pores to prevent them from exiting the exhaust system, the gas passes through the filter. However, because of its limited capacity, as with any other type of filter, the DPF must empty its trapped exhaust soot regularly to enable it to perform optimally. During this process, known as DPF regeneration, the accumulated exhaust soot in the DPF is burned off at a high temperature. The DPF must be able to regenerate itself whenever it is filled up with soot. Otherwise, the filter's health is threatened, and its service life may be reduced.
There are two types of regeneration. These are active and passive regeneration:
- Active Regeneration - This usually takes place when a vehicle is operated for a long time at extremely high speeds and is an automated process. The pressure sensors in the inlet and outlet end of the DPF system sense the presence of exhaust soot once the soot level in the filter reaches about 45%. At this level, the vehicle's engine management system (ECU) will initiate the injection of raw fuel to increase the temperature in the exhaust, which triggers the optimal conditions for active regeneration. Active regeneration needs no physical effort from vehicle owners or drivers.
- Passive Regeneration - Passive regeneration is also a fully automated process, and it is hardly noticeable to a vehicle owner or driver. However, it only happens when a vehicle's engine attains high temperatures, usually over 350ºC. The DPF is able to combust accumulated exhaust soot when the vehicle is driven normally under such temperatures.
Where Is The Diesel Particulate Filter Located?
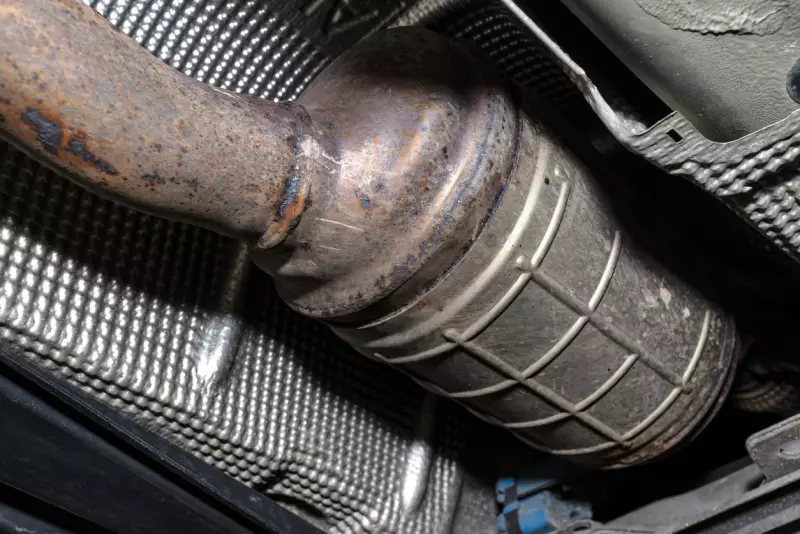

Vehicle DPFs are commonly located around the exhaust manifolds of diesel engines but are also positioned around the turbochargers instead of on the underbody in some cases. The main reason for placing it within the exhaust system is to aid in filtering out particulate matter resulting from incomplete fuel combustion. The DPF is closely located to the engine after the temperature sensor and is usually just ahead of the exhaust pipe and the NOx storage catalytic converter.
How to Tell If DPF Is Clogged
You can tell that your vehicle's DPF is clogged if you notice the following:
- The DPF engine management light (warning light) on the dashboard turns on - This is usually the first clue of a blocked diesel particulate filter. The sensors in your diesel engine vehicle can detect a clogged DPF and trigger the warning light to show up on the dashboard. The check engine light may also come up in some cases.
- Reduced or poor fuel economy - You will notice a reduced fuel economy because your vehicle engine will work harder with a clogged DPF, making you burn more fuel rapidly.
- Poor engine performance - When the DPF is clogged, it also blocks the exhaust and suffocates the engine,which can cause your vehicle to not accelerate properly
- Odd odors in the cabin - You can notice strong diesel odors in the cabin as a result of a blocked diesel particulate filter. This is because the built-up exhaust gas cannot escape, causing an unpleasant smell within the cabin. This is dangerous because it can also lead to fire.
- Difficulty starting the engine - The pressure within the engine can increase as a result of the excess built-up fumes due to a clogged DPF. This can lead to starting problems, and in some cases, the engine may refuse to start.
How To Avoid Blocked Diesel Particulate Filter Problems
Proper car maintenance is required to avoid having a blocked diesel particulate filter in your vehicle. The following are tips on preventive measures you can deploy to prevent or reduce the risk of a clogged DPF:
- Regular change of engine oil and proper engine maintenance. However, it is important to use the recommended engine oil for your vehicle because the service lifespan of DPFs is somewhat determined by the type of engine oil. Low sulfated ash, phosphorus, and sulfur (SAPS) or mid-SAPS engine oil are usually advised in engines with diesel particulate filters.
- Drive your vehicle for long distances so that the engine can attain its operating temperature and enable a complete DPF regeneration process. Driving short distances will continuously interrupt the regeneration process and lead to a blocked diesel particulate filter.
- Do not drive your vehicles at low revs. Although new trends encourage operating a car at low revs, this may not be good for DPFs. Driving at low revs implies your engine will not warm up to the level that will initiate the DPF regeneration process, and this can lead to a clogged DPF over time.
- Make using DPF cleaners a regular routine. These additives aid the burning of exhaust soots and can help in maintaining the DPF.
- Have your DPF checked by diagnostic equipment whenever you take your vehicle for servicing at your local car garage.
How to Clean Diesel Particulate Filter
You can clean your vehicle's diesel particulate filter in any of the following ways:
- Frequently rev the engine during long distance drives with intermittent high revs to foster recurring regeneration processes. Typically, diesel engines come with built-in DPF cleaners that automatically burn off excess exhaust soot when the engine is hot. This is known as passive regeneration. The active regeneration process will kick in even when you are not on the road long enough to complete a passive regeneration cycle. During active regeneration, the DPF system injects excess fuel, raising the exhaust temperature to a level capable enough to cause a complete combustion of the exhaust soot.
- Try any of the following methods if your vehicle's DPF system becomes too clogged to initiate a regeneration process or regenerate properly:
- Clean the DPF filter by spraying heated water on the opposite side of the exhaust flow using a pressure washer.
- Use a DPF cleaner to lower the combustion temperature of the exhaust soot to enable it to burn off seamlessly during regeneration.
- Pressure-blow compressed air into the DPF using a pressure gun to remove loose ash.
Seek the services of a professional diesel particulate filter (DPF) cleaning company if everything else, including the automatic regeneration process, manual cleaning, and chemical cleaners, fails to clean your vehicle's DPF system. Professional DPF cleaning services generally include removing all oil deposits, particulate matter, and loose ash from a vehicle's DPF system.