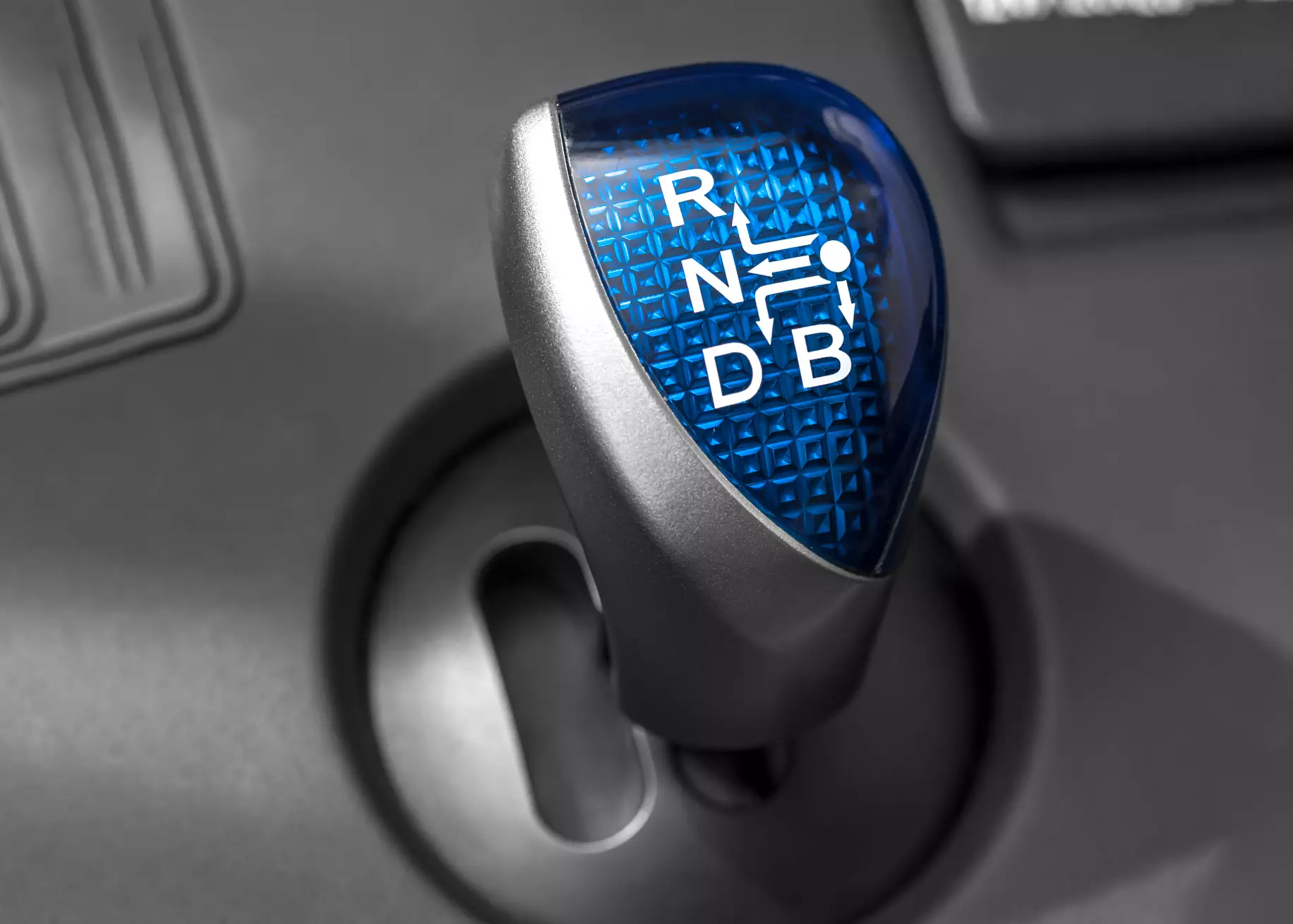
Like other types of automatic transmissions, the primary function of a continuously variable transmission (CVT) is to change the speed ratio between the engine and the wheels of a vehicle.
However, unlike traditional automatic transmissions, a CVT offers an infinite number of gear ratios within a specific range. This capability results in smoother operation and improved fuel efficiency. While CVTs provide a more seamless driving experience and better fuel economy, many drivers are concerned about their long-term reliability.

What Is a CVT Transmission and How Does It Work?
A Continuous Variable Transmission (CVT) is an automatic transmission that provides a smooth driving experience by offering an endless range of gear ratios. CVTs help improve engine performance and fuel efficiency by keeping the engine running at its best RPM for the current speed or load. You can often find CVTs in smaller cars, hybrid vehicles, and SUVs.
Unlike standard automatic transmissions that use gears to change speed, CVTs do not have a fixed number of gears. Instead, they use a pulley system that allows for smooth changes between high and low gears without any noticeable shifting. Most CVTs have two pulleys that can change their size and are connected by a belt or chain. They also have a hydraulic or electronic system to control the pulleys.
One pulley connects to the engine, and the other connects to the wheels. Each pulley has two cone-shaped parts that can move closer together or further apart, changing the size of the pulley. When the parts are close together, the belt rides higher, making the pulley larger. When the parts are further apart, the belt rides lower, making the pulley smaller. By adjusting the distance between the pulley parts, a CVT can change the gear ratio smoothly without any gear shifts.
Why Automakers Use CVTs?
Manufacturers prefer CVTs over traditional automatic transmissions for several reasons. Discussed below are some of the key reasons driving their preference:
- Improved fuel economy: VTs enhance engine performance by maintaining the optimal RPM for efficient speed, which helps reduce fuel consumption. By producing vehicles equipped with CVTs, manufacturers can comply with strict global emissions and fuel efficiency regulations.
- Cost Effectiveness: CVTs have a simple design with fewer moving parts than traditional automatic transmissions. Traditional transmissions use complex gear systems and hydraulic parts. This simpler design can lower manufacturing costs.
- Adaptability to Driving Conditions: CVTs can quickly change gear ratios to match different driving situations, like accelerating, cruising, or going uphill. This feature helps provide the right balance of power and fuel efficiency without the delays that come with regular gear shifts. Because of this, CVTs are a good choice for many consumer vehicles, especially in city driving.
- Improved Driving Experience: CVTs allow for smooth acceleration without the obvious gear shifts found in traditional automatic transmissions. This makes driving more comfortable for both the driver and passengers, especially in stop-and-go traffic. This makes CVTs attractive for mainstream vehicles like compact cars and hybrids.
- Compatibility With Hybrid Systems: CVTs work very well with hybrid vehicles because they effectively control power delivery between the gasoline engine and electric motor.
- Consumers Appeal For Efficiency and Comfort: With rising fuel prices and environmental awareness, consumers increasingly prioritize fuel-efficient vehicles. CVTs help manufacturers market cars as eco-friendly and cost-effective to operate.
Are CVT Transmissions Reliable?
Since their widespread adoption in the 2000s, people have debated the reliability of CVT systems. Early CVTs had a reputation for being unreliable. They often faced problems such as chain or belt wear, overheating, and premature failure, especially in high-torque situations.
However, modern CVTs have made significant improvements. Advances in design and materials have made CVTs much more reliable. For example, many newer CVTs use stronger steel belts or chains and better lubricants, which help reduce wear and increase their lifespan. New pulley designs and cooling systems also help prevent overheating, a common problem in older models.
Most CVTs in vehicles made from 2015 onward are reliable under usual driving conditions and can last between 100,000 to 150,000 miles or more with proper care. Despite these improvements, the reliability of a CVT can vary based on the vehicle brand, model, and maintenance.
For instance, CVTs from Toyota and Honda are generally regarded as dependable, while some Nissan CVTs, particularly in older Altima and Sentra models, have received criticism for durability issues.
Are CVT Transmissions Bad?
No, CVT transmissions are not inherently bad. However, whether they are a good choice for you depends on several factors, including your driving preferences, vehicle type, and expectations.
CVTs have unique characteristics that some drivers love and others dislike, and both early issues and modern improvements have shaped their reputation.
The question, 'Why are CVT transmissions bad?' began as a response to the criticisms of CVT systems by early adopters. For instance, early adopters of CVTs have been critical of their durability. Most of these CVTs had issues, such as chain or belt wear, overheating, and premature failure, making them a less reliable option compared to traditional automatic transmissions.
However, modern CVTs have been able to overcome these durability issues, and that's not all. These newer designs enable a smoother driving experience and improved fuel efficiency.
Common CVT Transmission Problems and Complaints
While CVTs transmission improves fuel efficiency and offer a better driving experience, they can have specific problems. Below are the most common CVT issues and complaints based on consumer feedback:
- Slipping: This occurs when the engine revs without a corresponding increase in vehicle speed. This reduces performance and may lead to overheating if not addressed.
- Overheating: This is caused by inadequate cooling systems, degraded fluid, or excessive stress from aggressive driving.
- Premature failure: This leads to the total breakdown of the CVT system. It may be caused by belt/chain failure, internal component wear, or manufacturer defect.
- Engine Noise: High RPMs during acceleration create a loud, droning noise. This is especially noticeable in budget vehicles that have less sound insulation.
- Rubber Band Effect: Some drivers do not like how the CVT keeps the engine at a high RPM when they accelerate. This makes the engine feel separate from the vehicle’s speed.
How To Extend the Life of a CVT Transmission
Extending the life of a CVT requires proactive maintenance, mindful driving habits, and attention to manufacturer recommendations. Below are practical steps to help ensure your CVT is in good condition:
- Change CVT fluid on time: Inadequate fluid can cause overheating, slipping, or belt/chain wear, leading to costly repairs. As such, it is advised that you replace your CVT fluid on time as specified in your vehicle’s manufacturer’s manual. For example, Honda recommends 30,000 miles for Civic CVTs, while Toyota recommends around 60,000 miles for Corolla.
- Use manufacturer-specified fluid: Always use the exact CVT fluid recommended by the manufacturer. CVT fluids are specially formulated for the unique demands of a brand's belt/chain and pulley systems. Therefore, using an incorrect fluid can damage the transmission.
- Avoid aggressive driving: Aggressive driving, such as rapid acceleration and sudden braking, may damage your CVT transmission.
- Monitor warning signs: When you notice common issues such as jerking, shuddering, slipping, dashboard warning lights, and unusual noise, take the vehicle to a qualified mechanic immediately.
- Schedule regular maintenance: One of the answers to the question, ‘Why CVT transmissions are bad?’ is lack of maintenance. You can extend the life of your CVT transmission by scheduling and performing regular maintenance. Always ensure that this routine maintenance is performed by a mechanic who is familiar with the technology.
Is a CVT the Right Choice for You?
Whether a CVT is a good choice for you depends on your driving needs, preferences, and priorities. CVTs offer distinct advantages, making them particularly suitable for city commuting, fuel-conscious drivers, and those living in areas with high fuel prices. They are also an excellent option for consumers who prioritize eco-friendly vehicles.
Vehicles with CVTs offer a relaxed and effortless driving experience, although they may not be ideal for driving in harsh conditions. Additionally, CVTs work exceptionally well with hybrid powertrains, optimizing the power delivery between the gasoline engine and electric motor for maximum efficiency and smoothness.
Finally, CVTs typically come with a warranty and tend to have a higher resale value compared to most traditional automatic transmission vehicles. CVT transmissions offer a smoother, more fuel-efficient driving experience and are especially well-suited for modern, eco-conscious vehicles. While early models struggled with reliability, advancements in design and maintenance practices have made today’s CVTs a smart and dependable choice for many drivers