The AC compressor in a vehicle is an important component of the air conditioning system. The compressor puts refrigerant under pressure and sends it through the AC system to cool the cabin of your vehicle.
Compressors, should last 10 years or more, but they can get damaged in accidents, or part of it, like the clutch, can go bad and require replacement. Symptoms of a failing compressor include:
- Warm air entering the cabin of the car when the AC is turned on.
- Squealing or whining noises from the engine.
- A coolant leak under the car.
AC compressor replacement is not inexpensive but varies according to the make and model of the vehicle. Taking your vehicle to a mechanic will likely cost $1,200-$2,000 with parts and labor. Check first to make sure your vehicle isn’t still under warranty because you may get a compressor for free if it is. Also, determine if a third-party AC compressor replacement (one that is not from your vehicle’s manufacturer) will void any warranty or service contract in effect.
How Does An AC Compressor Work?
Driven by a belt connected to the engine crankshaft, the compressor has pistons that suck in refrigerant gas and send it to the condenser, where the gas is changed to a liquid. The liquid is moved through hoses to the evaporator, which provides cool air to the vehicle’s occupants.
Where is The AC Compressor Located in a Car?
Its exact location can vary depending on the make, model, and design of the vehicle, but here are some common places where you might find the AC compressor:
Front of the Engine: The AC compressor is often mounted at the front of the engine and is usually driven by a belt connected to the engine's crankshaft. This is the most common placement and is easily identifiable by looking for a component with a belt and pulleys. It will also have metal and rubber hoses connected to it, which lead to other parts of the air conditioning system.
Lower Side of the Engine: In some vehicles, especially those with transverse (sideways) mounted engines or in vehicles with compact engine bays, the compressor might be located on the lower side of the engine. It might be slightly more challenging to spot from the top and could require looking from underneath the vehicle.
Beside the Radiator: In a few designs, the compressor might be situated close to the radiator or the front grille to facilitate easier access to fresh air, although this is less common.
When to Replace AC Compressor in a Car
Your check engine light should illuminate on the dash if there’s an issue with your AC system, but that’s not always the case. If your system isn’t delivering cool air to the cabin, you may diagnose an issue with the compressor through the following:
- Wiring that is disconnected, chafed, or broken can interrupt the flow of electricity to your compressor. Check to ensure the connections are clean and complete, then inspect the length of the wire for any breaks.
- The control board used to set the AC level in the vehicle can go bad. You may find out when the blower doesn’t activate, or it comes on too often and doesn’t hold the desired temperature. Check this unit for blown fuses or broken wiring before trying to replace the compressor.
- A leak under your vehicle can signal a break in the refrigerant system. Your compressor may be working, but if the refrigerant leaks, you won’t get cool air in the cabin. See warnings about handling freon or another refrigerant before replacing any part of the AC system.
- A bad clutch (the part that accepts power from the engine to run the compression process) is a common point of failure for the compressor. You may hear a screeching or whining sound when you turn on your AC, which can mean the clutch is not working properly.
Bad AC Compressor Symptoms
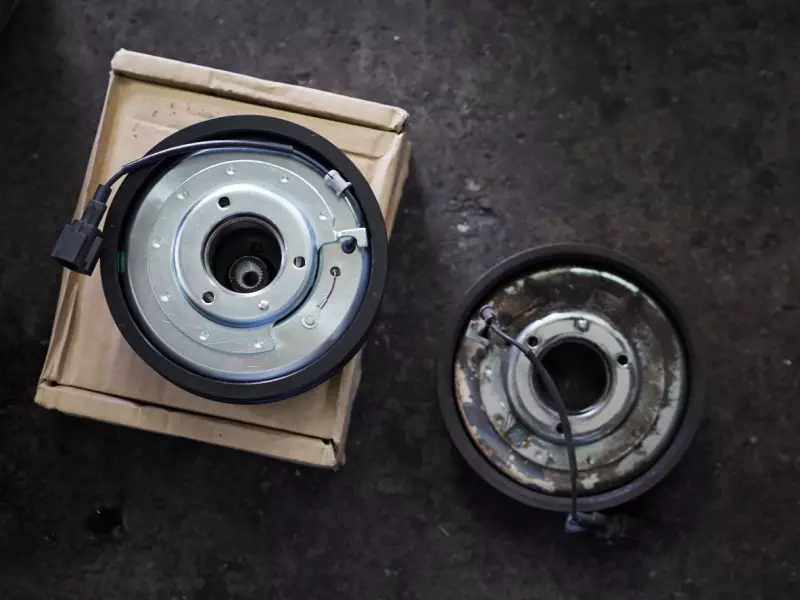

The clutch is the compressor part most likely to fail. Test the compressor clutch by attaching a wire equipped with alligator clips on both ends to the car battery. Attach it to the battery terminal with one clip and put an open safety pin in the other clip. Pierce the black (live) compressor power wire with the safety pin and listen for the click of the compressor clutch. If you hear a click every time the wire is pierced, the clutch is in good operating condition.
If the clutch is not the issue, check the belt from the compressor to the crankshaft. It should be taut but able to move and without any signs of wear. A belt that doesn’t grab correctly will wear out quickly. This is an inexpensive part to replace, so it’s a good starting point in diagnosing a compressor issue.
How to Replace the AC Compressor
Before attempting to replace your compressor, you must understand the legal issues and hazards involved in handling the refrigerant. “Freon” is the catch-all name for vehicle refrigerants, but there are different types. Check for a sticker or label inside the hood of your car that tells what kind you have. Understand that these substances are greenhouse gases whose handling is controlled by law, so releasing any into the environment is illegal (and there’s a cash award available to anyone who reports illegal releases, another disincentive for DIY mechanics).
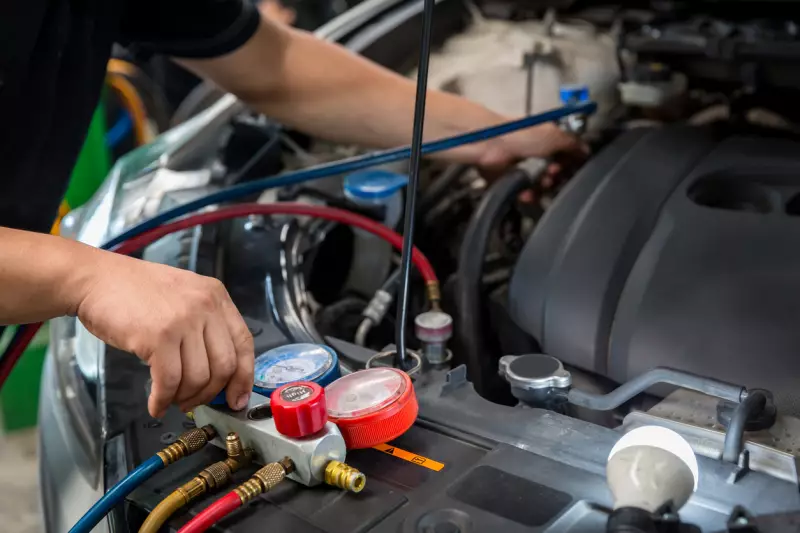

Refrigerants are also hazardous to people, so you should not allow them to come into contact with your skin, eyes, or to be inhaled. States may require certified technicians to handle this aspect of the replacement.
These are the basic steps to AC compressor replacement:
- Determine if your refrigerant is pure or not. If it’s pure, it can be reused; if not, it must be disposed of properly.
- Ensure the car’s AC and heat controls are off, and disconnect the battery.
- Start with pumping the refrigerant out of the system and into an approved container.
- Locate and remove the compressor belt (start by loosening the tensioner pulley).
- Locate and remove the electrical connections to the compressor.
- Disconnect the refrigerant lines and cap them to avoid releasing any residual freon into the environment. Clean the refrigerant system.
- Unbolt and remove the compressor. Keep track of bolts and their proper locations.
- Replace any seals. Consider replacing the accumulator as well to reduce another potential source of issues.
- Reverse the process, starting with bolting the new compressor into position. Replace the freon with pure refrigerant.
How Long Does It Take to Replace AC Compressor?
AC compressor replacement in a car typically requires about 4-6 hours for a professional mechanic to complete. This time can vary depending on the make and model of the vehicle, the complexity of the engine layout, and the specific tools and equipment available. Some vehicles might allow for easier access to the compressor, potentially reducing the time needed, while others may have more compact or complex layouts that can extend the required time.
Additionally, if the system needs to be thoroughly inspected, cleaned, or if other components also need to be replaced or serviced (like the receiver drier or expansion valve), this can add to the overall time needed to complete the job. Experts say it’s imperative to work quickly on the AC system so that potential contamination of the system is minimized.