The car brake system is the first line of defense and safety for all vehicles. Through operation, it prevents collisions and grazing and helps avoid unwarranted impacts whenever possible. To perform its function effectively, the components in a brake system must be in excellent working order. That is brake rotors, pads, lines, and shoes. If even one of the parts is worn out, the driver’s safety will be compromised. Brake rotors, particularly, are the surfaces on which the brake pads are pressed upon. These rotors are made of high-density iron and can last for thousands of miles. That does not mean they cannot fail as they still require maintenance and should be replaced at between 50,000 and 70,000 miles of use on average.
What Are Brake Rotors?
Brake rotors are metallic-type discs linked to the wheels' hubs. These spin alongside the wheels while the pads remain in one place. They are held on each side of the rotors by the brake calipers. Upon pressing the pedal, the calipers exact the same force against the pads, which also press against the rotors. The friction created between the pads and the rotor at each wheel is what causes the vehicle to slow down and eventually stop. It is worth noting there are four different types of rotors to choose from. Prior to buying or replacing rotors, it is advisable to know which is the best option for your required use-case. They are drilled, blanked, slotted, and drilled & slotted.
Drilled brake rotors allow water and heat to be dissipated from the rotor surface. This brake rotor also helps with stopping power by reducing brake fade, so it is appropriate for wetter climates. Plain or blank brake rotors are the typical options for new passenger vehicles. They are made from cast iron and can absorb an average heat level. They are reliable under normal circumstances but would not be advisable for aggressive driving as this relies on significant braking, hence a lot of heat. They are also much more likely to rust if they do not have finishes.
Slotted brake rotors are those that have slots rather than holes. These are used for larger commercial vehicles or passenger SUVs because they provide good stopping power. Their structure also allows gas and dust to escape, hence less stress. Slotted brake rotors offer more resistance to cracking. While these pads help aid in heat dissipation, it is minimal and their more jagged edges increase brake pad wear. They are an upgrade from the plain option, though and reduce brake fade during aggressive braking.
Drilled and slotted brake rotors allow gas, moisture, and dust to escape, so there is adequate, consistent contact with brake pads. Combining a drilled brake rotor that runs cooler and the slotted alternative that keeps the surface clean gives extra durability. Unlike plain rotors, drilled and slotted ones look great, though they do not rust as easily. It's important to note that brake pads wear more quickly on slotted and drilled rotors and more frequent replacement will be required.
What Are Brake Rotors Made Of?
Though the Brake rotors may be made of different materials, such as cast iron, steel, layered steel, aluminum, ceramic, and high carbon. Cast iron is the most common material used for brake rotors. It works for typical passenger vehicles, though the additional weight means it does not work well for performance cars. Steel rotors are preferred for track racers due to their lighter weight and higher heat tolerance. Layered steel rotors are made by setting sheets of steel on one another and laminating them. This rotor design is a favorite among those in performance circuits because of its lightweight performance. High-carbon rotors are composed of iron but have a significant carbon volume in the metal mixture. They do not fracture under high stress. These also have less noise and vibration. Unfortunately, these rotors tend to be pricey compared to the others. Ceramic brake rotors have an impressive heat absorption rate and release capacity. It is the best material for brake rotors, although it is also expensive. Finally, there are aluminum rotors, which are lightweight and can release heat quickly. The melting point, though, is lower than other materials. These are used for motorcycles that do not concentrate heat for a significant amount of time, unlike commercial vehicles.
What Do Brake Rotors Do?
Brake rotors begin operation immediately after the driver presses the brake pedal. When that happens, the force is related to the pads via hydraulic pressure using brake fluid. The pads are forced to compress against the rotors with the same amount of energy relayed by the foot depressing on the pedal. Each wheel has one rotor, so when the driver engages the brake system, all four rotors slow the wheel's speed down.
The process of slowing wheels through friction results in intense heat. Brake rotors are made of materials that can resist the heat up to a point. Some have holes or slots that allow for the dissipation of heat. When the driver lifts their foot off the brake pedal, the hydraulic pressure reduces against the pads. The pads stop pressing on the rotors, allowing the wheels to move freely without restrictions. From the way that brake rotors operate there are particular things which cause wear and ultimate failure. Sudden stops like panic or emergency braking at high speed may lead to rotor wear. Excess wear is caused by friction from the pad grabbing the rotor, resulting in high heat and wear levels. Constantly putting one’s foot on the brake may also cause wear because of the stress of consistent friction. This can happen absent-mindedly when driving down a hill, and constantly pressing a brake for an extended period leads to intense temperatures and brake fade, making it difficult to stop. As opposed to using the brakes down slopes, it may be better to switch to lower gears to slow the vehicle down. This is also known as engine braking.
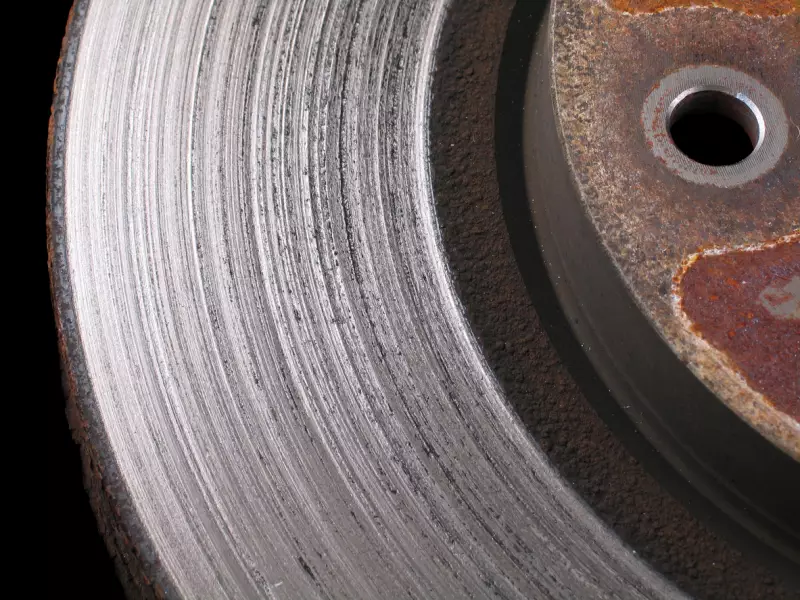

Driving for an extended period on worn brake pads will also cause damage. As the pads deteriorate, metal-to-metal contact increases upon application of the brakes. That contact is highly stressful and can result in deep grooves or cracks in the rotor.
Rotors are durable, but they break down like any other component, as evidenced. Driving using damaged brake discs is very dangerous, considering it can lead to increased stopping distance or an ultimate loss of braking ability. Some common signs that the brake rotors need to be changed include brake squeaking or grinding noises during light or hard braking. This is very hard to miss, especially during high-traffic situations when the vehicle is traveling at low speeds. If the brake pedal judders during braking, that’s also a sign that the rotors may be shot. Alternatively, it could be a problem with the pads being soiled by dirt or debris. Visual inspections of the brake rotors will also reveal their condition. Rotos that have significant wear have grooves or cracks. Unfortunately, if the rotor shatters, it may cause a complete wheel lockup, causing the vehicle to lose control and potentially roll at high speed.
How Many Brake Rotors Does a Car Have?
All vehicles have four brake rotors, one for every wheel. Older cars may have drum-type brakes in the rear and the front. The more modern passenger vehicles have brake rotors on all wheels or disc brakes in the front while the drums are on the rear wheel. Commercial vehicles, such as 18-wheelers, may have ten brake rotors. The reason is an 18-wheeler has five axles, each with two brake sets. That makes a total of ten brakes, hence ten rotors.
Brake Rotor Replacement Cost
The cost of replacing a brake rotor depends on several factors, such as the vehicle's brand, make and model, and the type of driving exercised. Usually, Japanese-made models such as Toyota or Nissan will cost less compared to German or American-made car parts. It is also because the systems on a German model may be different compared to Japanese or American brake structures, so it would take more time to replace these, hence the price hike. It also depends on what the vehicle is being used for. For example, city driving does not significantly stress brake rotors, but heavy-duty work or towing does. The vehicle owner would have to get rotors suited for that work. Overall, rotors by themselves typically range from $60 to $180 per set. If the owner includes the labor cost, it could run from between $160 to $480.
What to Do With Old Brake Rotors
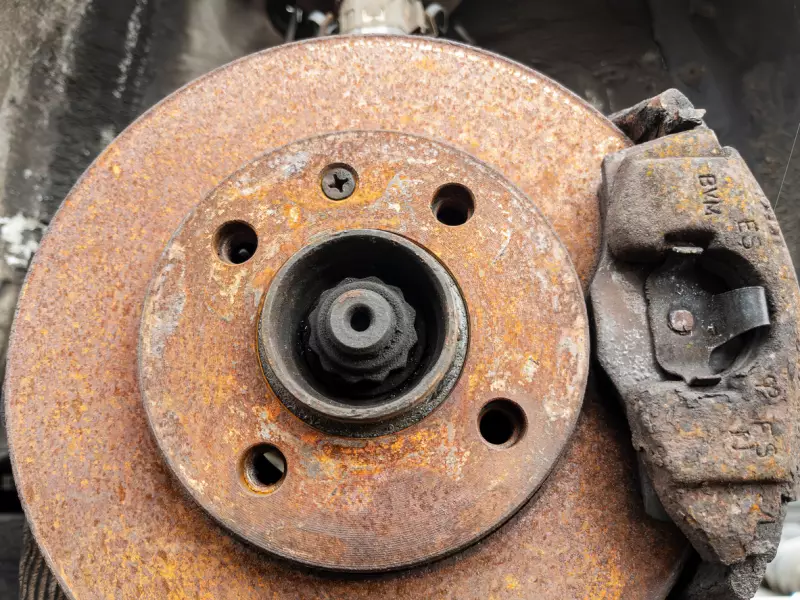

Vehicle owners can choose what to do with their old rotors. They can throw them out or recycle them. Rotors not too badly off can be sold to scrap or salvage yards. Old calipers may also be thrown away, but the brake fluid needs to be drained. Brake rotors can be repurposed as household knick knack pieces of art. It all depends on the owner’s imagination.
Conclusion
Brake rotors are a crucial part of the braking assembly and should be assessed with the same frequency as brake pads. There are several types of rotors, depending on their use. Most passenger vehicles use plain brake rotors made from cast iron. Some rotors have drilled holes to release heat and debris. Due to the increased heat loads, these rotors tend to bear, these are for heavy-duty or performance use. Though rotors are durable, they should be replaced within 50,000 to 70,000 miles of use to keep wear at a minimum. Old rotors can be resold to scrap yards or repurposed in the home.